Stepper motors can be driven in two different patterns or sqeunces. namely,
►Full Step Sequence
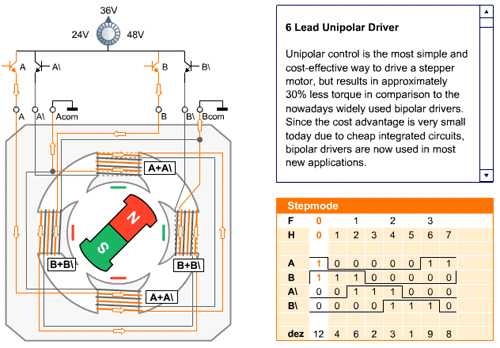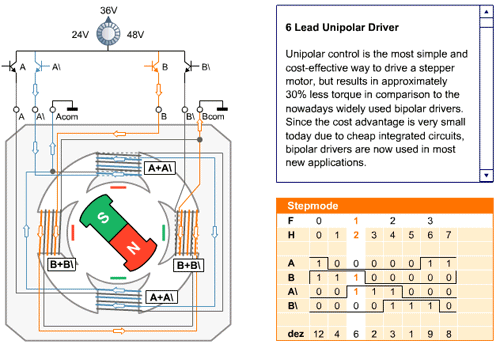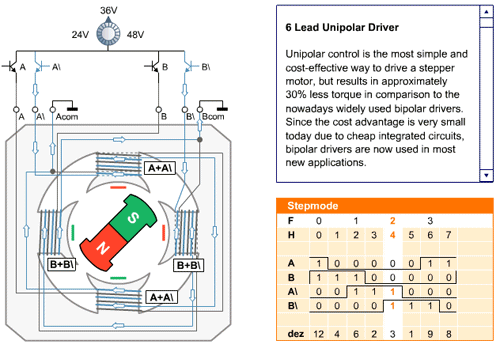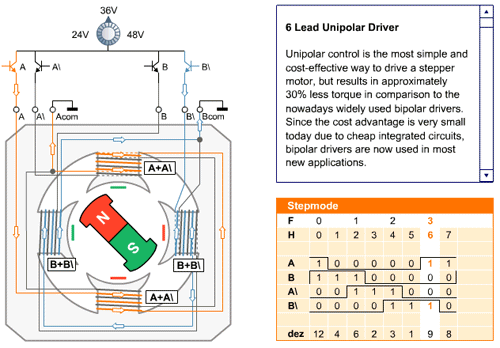
In the full step sequence, two coils are energized at the same time and motor shaft rotates. The order in which coils has to be energized is given in the table below.
The working of the full mode sequence is given in the animated figure below.
►Half Step Sequence
In Half mode step sequence, motor step angle reduces to half the angle in full mode. So the angualar resolution is also increased i.e. it becomes double the angular resolution in full mode. Also in half mode sequence the number of steps gets doubled as that of full mode. Half mode is usually preffered over full mode. Table below shows the pattern of energizing the coils.
The working of the half mode sequence is given in the animated figure below.

►Step Angle
Step angle of the stepper motor is defined as the angle traversed by the motor in one step. To calculate step angle,simply divide 360 by number of steps a motor takes to complete one revolution. As we have seen that in half mode, the number of steps taken by the motor to complete one revolution gets doubled, so step angle reduces to half.
As in above examples, Stepper Motor rotating in full mode takes 4 steps to complete a revolution, So step angle can be calculated as...
Step Angle ø = 360° / 4 = 90°
and in case of half mode step angle gets half so 45°.
So this way we can calculate step angle for any stepper motor. Usually step angle is given in the spec sheet of the stepper motor you are using. Knowing stepper motor's step angle helps you calibrate the rotation of motor also to helps you move the motor to correct angular position.
►Step Sequence for 2-wire control of Unipolar stepper motor
As seen in above explanation, In every step of the sequence, two wires are always set to opposite polarities. Because of this, it's possible to control steppers with only two wires instead of four, with a slightly more complex circuit. The stepping sequence is the same as it is for the two coils A and B, and the opposite polarity value is given to A\ and B\. The sequence is given in the table below:
►Step Sequence for Bipolar stepper motor
Bipolar motor has simpler construction. It has two windings with no center taps and a permanent magnet at the center just like unipolar stepepr motors. Being simpler in contruction, the stepping sequence is a little complex, as the power for both the coils has to be controlled in such a way that the polarity of the poles get reversed. This polarity sequence is shown in the table below.
The above polarity sequence can be interpreted in terms of logic levels for microcontroller by activating one coil at a time as shown in the table below.
We have now learnt most of the necessary things regarding a stepper motor. In the next section we will discuss about the various techniques to interface a stepper motor.
- Full Step Sequence
- Half Step Sequence
►Full Step Sequence
In the full step sequence, two coils are energized at the same time and motor shaft rotates. The order in which coils has to be energized is given in the table below.
| Full Mode Sequence | ||||
| Step | A | B | A\ | B\ |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
The working of the full mode sequence is given in the animated figure below.

►Half Step Sequence
In Half mode step sequence, motor step angle reduces to half the angle in full mode. So the angualar resolution is also increased i.e. it becomes double the angular resolution in full mode. Also in half mode sequence the number of steps gets doubled as that of full mode. Half mode is usually preffered over full mode. Table below shows the pattern of energizing the coils.
| Half Mode Sequence | ||||
| Step | A | B | A\ | B\ |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
The working of the half mode sequence is given in the animated figure below.

►Step Angle
Step angle of the stepper motor is defined as the angle traversed by the motor in one step. To calculate step angle,simply divide 360 by number of steps a motor takes to complete one revolution. As we have seen that in half mode, the number of steps taken by the motor to complete one revolution gets doubled, so step angle reduces to half.
As in above examples, Stepper Motor rotating in full mode takes 4 steps to complete a revolution, So step angle can be calculated as...
Step Angle ø = 360° / 4 = 90°
and in case of half mode step angle gets half so 45°.
So this way we can calculate step angle for any stepper motor. Usually step angle is given in the spec sheet of the stepper motor you are using. Knowing stepper motor's step angle helps you calibrate the rotation of motor also to helps you move the motor to correct angular position.
►Step Sequence for 2-wire control of Unipolar stepper motor
As seen in above explanation, In every step of the sequence, two wires are always set to opposite polarities. Because of this, it's possible to control steppers with only two wires instead of four, with a slightly more complex circuit. The stepping sequence is the same as it is for the two coils A and B, and the opposite polarity value is given to A\ and B\. The sequence is given in the table below:
| 2-wire Mode Sequence | ||
| Step | A | B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
►Step Sequence for Bipolar stepper motor
Bipolar motor has simpler construction. It has two windings with no center taps and a permanent magnet at the center just like unipolar stepepr motors. Being simpler in contruction, the stepping sequence is a little complex, as the power for both the coils has to be controlled in such a way that the polarity of the poles get reversed. This polarity sequence is shown in the table below.
| Polarity Sequence | ||||
| Step | A | A\ | B | B\ |
| 0 | +ve | -ve | -ve | -ve |
| 1 | -ve | -ve | +ve | -ve |
| 2 | -ve | +ve | -ve | -ve |
| 3 | -ve | -ve | -ve | +ve |
The above polarity sequence can be interpreted in terms of logic levels for microcontroller by activating one coil at a time as shown in the table below.
| Step Sequence | ||||
| Step | A | A\ | B | B\ |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
We have now learnt most of the necessary things regarding a stepper motor. In the next section we will discuss about the various techniques to interface a stepper motor.
No comments:
Post a Comment